Committed to providing valuable information
Easy to find a blog that aligns with your specific interests and needs
Join our Community
Join us on our journey towards a healthier world
Health & Wellness blogs
Our health and wellness blog offers a wide range of informative and insightful articles that cater to different topics related to natural remedies, fitness, and well-being. From nutrition and exercise to mental health and stress management, our blog aims to provide readers with valuable information that can help them make positive changes in their lives.
To make it easier for our readers to navigate and find the content that interests them, we have included a filtering option where they can select the category they want to explore or search for specific keywords. Our blog is regularly updated with fresh and relevant content written by experts in their field, ensuring that our readers receive accurate and up-to-date information. We believe that a healthy lifestyle is essential for overall well-being, and our goal is to provide our readers with the knowledge and tools they need to achieve their health and wellness goals.
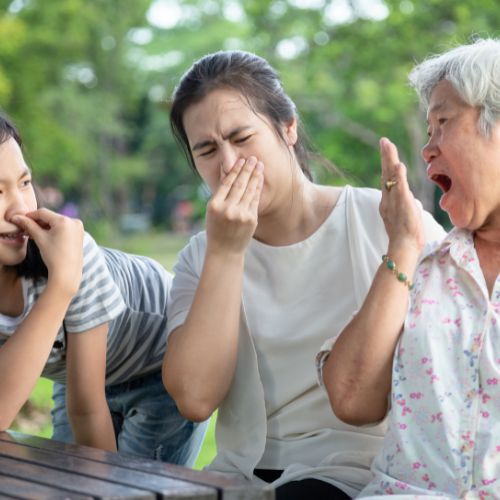

Unlock the secrets of nature’s potent solutions for wilderness challenges. Equip yourself for unexpected adversities!
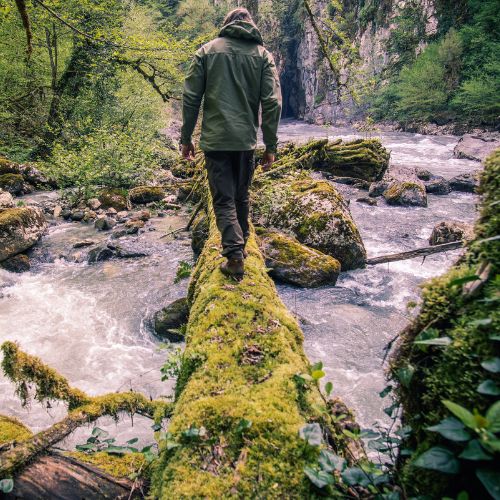

Unlock the secrets of nature’s potent solutions for wilderness challenges. Equip yourself for unexpected adversities!

Discover the Mediterranean Diet’s benefits with a comprehensive meal plan, foods list, and expert tips on whole grains, healthy fats, and plant-based eating.
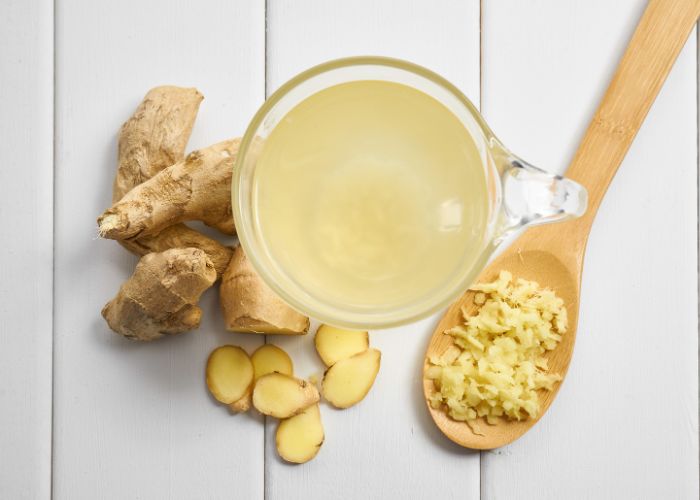

Discover home remedies that offer a holistic approach to healing, addressing not only the symptoms but also the root causes of various health issues.

Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a range of developmental disorders that affect communication, behavior, and social interaction. Learn more.
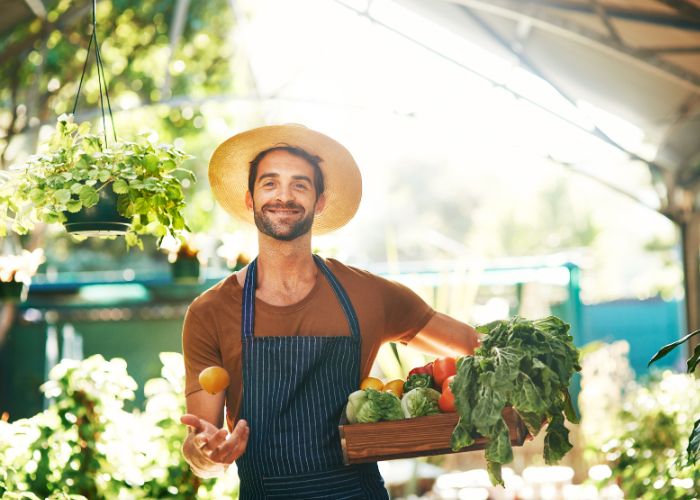

Discover the comprehensive guide on healthy living and lifestyle, where we delve deep into the core aspects that contribute to a fulfilling and enriching life.
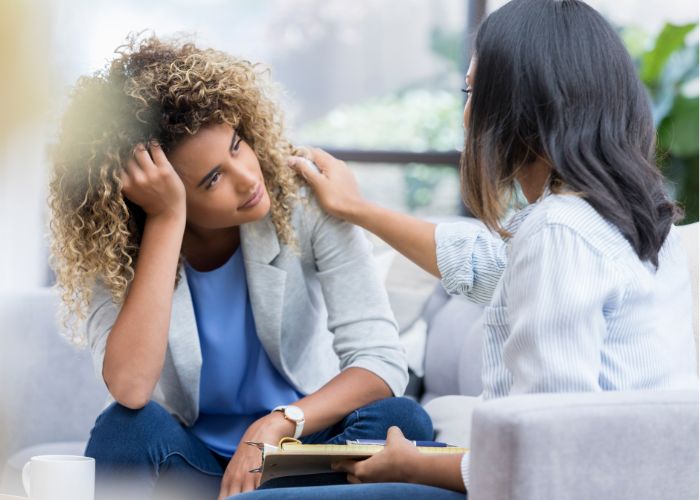

Discover the guide that aims to provide a thorough understanding of mental health and its various aspects with Writers’ recipe guides and tips.
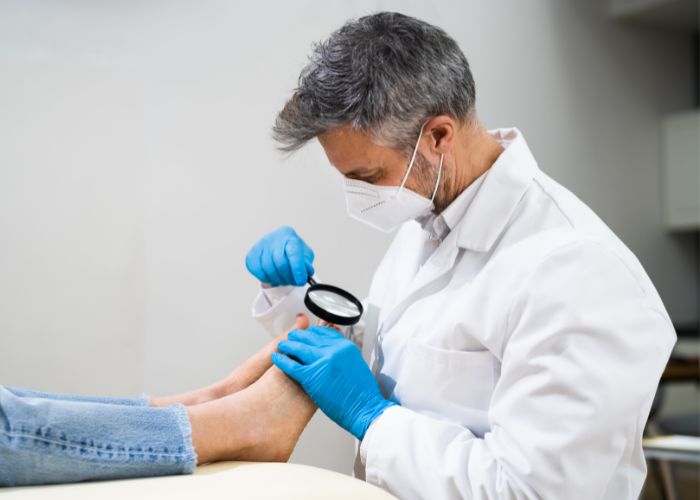
Discover the top 7 treatment options for ingrown toenail pain & learn about the different options to alleviate the pain and discomfort caused by this common foot condition.
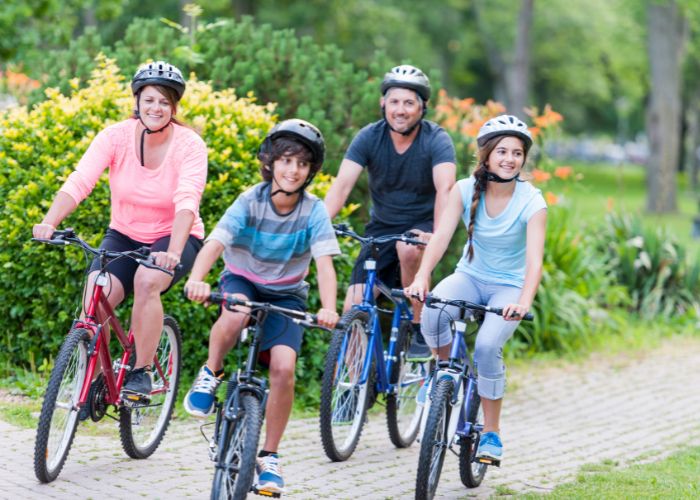

Biking With Varicose Veins – Is It Dangerous? Table of
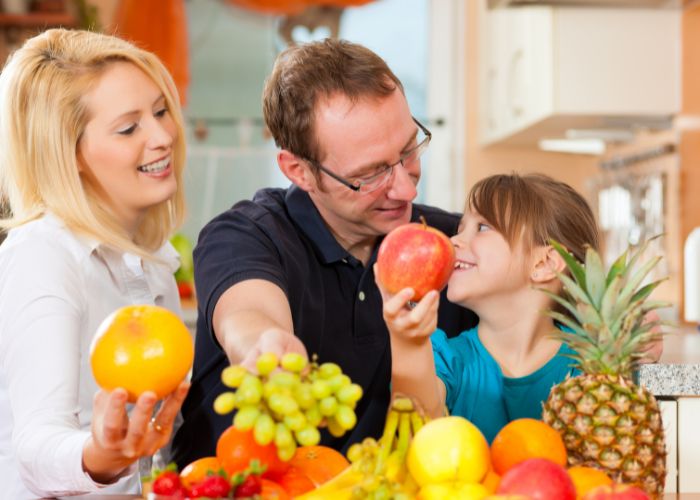

This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with valuable insights into the world of nutrition and diet, helping you make informed choices to attain ideal health and wellness.
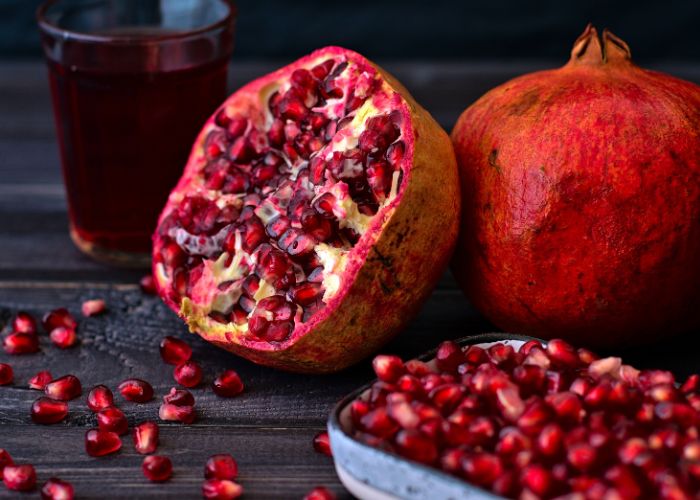

Pomegranates helps you maintain cholesterol levels intact, reduces arterial plaques those which are useful to battle against arthritis, osteoporosis, skin allergies, sore throats, skin disorders, urinary tract infections, osteoarthritis, digestive disorders, blood impurities and diabetes.

Discover common causes for a loss of appetite and learn healthy tips which you can use without guilt to improve your appetite.

Discover the Mediterranean Diet’s benefits with a comprehensive meal plan, foods list, and expert tips on whole grains, healthy fats, and plant-based eating.

This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with valuable insights into the world of nutrition and diet, helping you make informed choices to attain ideal health and wellness.

Discover the comprehensive guide on healthy living and lifestyle, where we delve deep into the core aspects that contribute to a fulfilling and enriching life.

Pomegranates helps you maintain cholesterol levels intact, reduces arterial plaques those which are useful to battle against arthritis, osteoporosis, skin allergies, sore throats, skin disorders, urinary tract infections, osteoarthritis, digestive disorders, blood impurities and diabetes.

Unlock the secrets of nature’s potent solutions for wilderness challenges. Equip yourself for unexpected adversities!

Unlock the secrets of nature’s potent solutions for wilderness challenges. Equip yourself for unexpected adversities!

Discover home remedies that offer a holistic approach to healing, addressing not only the symptoms but also the root causes of various health issues.

Discover the top 7 treatment options for ingrown toenail pain & learn about the different options to alleviate the pain and discomfort caused by this common foot condition.

Discover common causes for a loss of appetite and learn healthy tips which you can use without guilt to improve your appetite.
Night-bunion-splintBig-toe-straightener-bunion-brace-for-bunion-pain-relief.jpeg)
Discover and learn the most common symptoms and the 5 treatment options for bunions and the devices that can be used to alleviate the suffering.
Cant find what you're looking for?
Search our Heath & Wellness Articles


